In 2023, generative AI gained significant traction, capturing the attention of business leaders globally. No doubt, the anticipated impact of generative AI on businesses has been substantial, with meaningful changes expected for workforces across industries.
According to the latest annual McKinsey Global Survey on AI, one-third of respondents report that their organizations are already using generative AI regularly in at least one business function – representing 60 percent of organizations that have adopted AI. Moreover, 40 percent of these organizations plan to increase their overall AI investment due to generative AI, and 28 percent say that it is now a key topic on their board’s agenda. The application of Gen AI has been common across marketing and sales, product and service development, and service operations, such as customer support and back-office functions, signaling that companies are focusing on areas where they see the most value.
Microsoft, a leader in this technological shift, has integrated generative AI across its suite of business applications, including Microsoft Dynamics 365, Viva Sales, and the Power Platform. Through Copilot, Microsoft empowers users to enhance content creation, brainstorm ideas, and organize information directly within their workflows.
If your organization is considering Copilot in Dynamics 365 or Copilot in Power Platform, you may have questions around functionality, data security, and practical applications, this blog answers common questions to help guide your exploration.
Microsoft Copilot vs ChatGPT: Understanding the differences
While ChatGPT is a large language model (LLM) developed by OpenAI, designed for broad, general-purpose interactions, Microsoft Copilot is more tailored to enterprise needs. Built for business processes, Copilot is optimized to use your specific business data, security protocols, and contextual relevance to suggest actionable insights and responses, Integrated within Microsoft’s suite of business applications like Dynamics 365, Microsoft 365 (Word, Excel, etc.), and Microsoft Power Platform, Copilot is designed to enhance productivity and automate tasks within these tools. Its primary role is to assist users in generating content, analyzing data, automating workflows, and providing real-time insights based on the context of the application in use.
Here’s what makes Microsoft Copilot unique:
- Contextual responses: Copilot generates responses based on your business data, such as emails, documents, or CRM records, making its suggestions task-relevant and more actionable.
- Data security: Your business data remains secure within your organization’s tenancy, ensuring that LLM usage is limited to contextual relevance without being used for model training.
- Enterprise-grade security: Hosted on Microsoft Azure OpenAI Service, Microsoft Copilot adheres to high standards of security, compliance, and privacy.
Explore more: Meet Dynamics 365 Copilot – transforming business operations
Copilot in Dynamics 365 and Power Platform: How does it work?
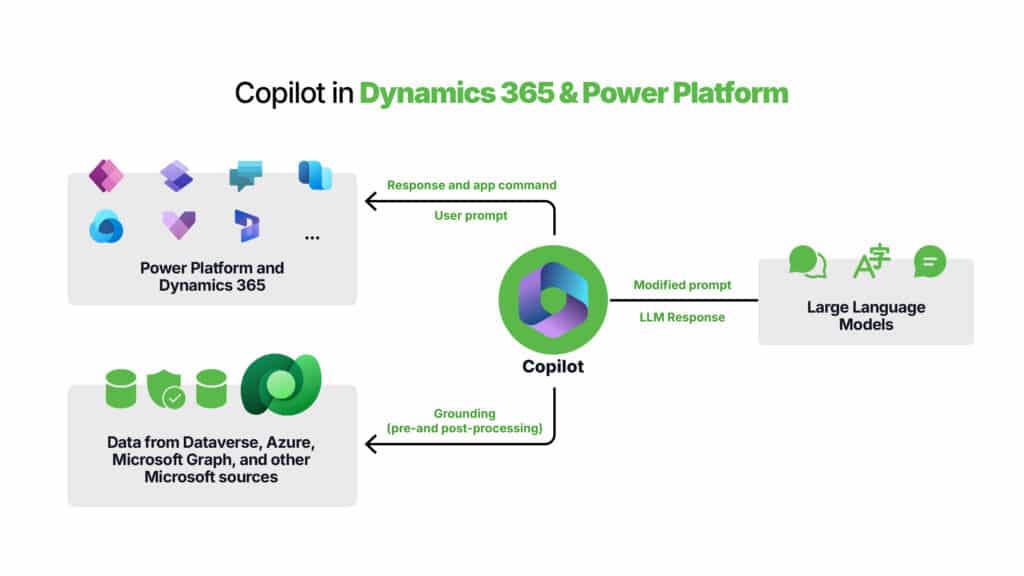
Copilot in Power Platform and Dynamics 365 uses foundation models with proprietary Microsoft technologies to transform your business data into task-specific insights:
- Search integration: Bing and Microsoft Azure Cognitive Search enables Copilot to access relevant information from organizational data (e.g., manuals, documents). Applications like Microsoft Power Virtual Agent (now rebranded to Microsoft Copilot Studio) and Dynamics 365 Customer Service use this retrieval-augmented generation approach as a step before calling a large language model (LLM).
- Business data: Copilot is seamlessly integrated with Dynamics 365, Viva Sales, Power Platform, and Microsoft Dataverse to help you access and retrieve your stored business information.
- Microsoft Graph API: The Microsoft Graph API enriches prompts by incorporating contextual information from customer signals, including data from emails, chats, documents, meetings, and more.
Behind the scenes: How does Microsoft Copilot work?
Now let’s see how Microsoft Copilot works. Copilot requests an input prompt from a user in an app (such as Microsoft Power Apps or Microsoft Dynamics 365 Sales ). When you input a prompt, Copilot first preprocesses it with “grounding,” which refines the query to improve relevance. It then uses Microsoft Graph and Dataverse to bring in contextual information specific to your business, ensuring that only authorized data is accessible.
This process begins by making a call to Microsoft Graph and Dataverse to retrieve enterprise data based on the permissions you’ve consented to for using your business content and context. Information is further grounded through documents and data available to authenticated users via role-based access controls.
For example, an employee querying the intranet about benefits would only receive information from documents relevant to their role. This retrieval technique, called retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), enables Copilot to provide precise information to the LLM by combining user-specific data with other sources, such as knowledge base articles, for a more refined prompt.
Once the LLM generates a response, Copilot conducts post-processing steps, including further grounding with Microsoft Graph, responsible AI checks, and security, compliance, and privacy reviews. Command generation is also included as part of this refinement process.
Finally, Copilot delivers a suggested response to the user and sends commands back to the relevant applications, allowing a human-in-the-loop to review and validate. Through this iterative orchestration of services, Copilot ensures that the results are relevant, accurate, and secure for your business needs.












