Did you know that a whopping 77% of business executives believe generative AI will have a bigger impact than any other technology over the next 3-5 years? Gen AI tools like ChatGPT, Google Gemini, and Microsoft Copilot are changing the game from speeding up code-writing and generating content to simplifying daily tasks. But with great power comes great responsibility and one big, raising a burning question: What’s ethical and what’s not when it comes to using generative AI?
Adding to the urgency, a recent study reveals that 56% of business executives are either unaware or unsure if their organizations even have ethical guidelines for using generative AI. This shocking statistic exposes a major gap in understanding and preparation, signaling a clear call to action for businesses to take generative AI ethics seriously in the age of data and AI.
In this blog, we’ll break down what AI ethics really mean, cover the five pillars of the ethics of generative AI, and share how your business can set up for success in this new era. Keep reading to get the full picture.
What is AI ethics? The moral compass for generative AI development
Ethics in AI refers to the guidelines and principles that govern the development and use of artificial intelligence in a way that is fair, transparent, accountable, and beneficial to society. As AI technology continues to evolve rapidly, the ethics of AI ensure that AI systems operate responsibly, avoiding harm and respecting fundamental human rights. These principles cover everything from the way data is collected and used to the potential societal impact of deploying AI technologies. Key areas of concern include privacy, fairness, accountability, and bias prevention.
AI governance plays a critical role in establishing frameworks and policies that uphold ethics in AI. Responsible AI governance ensures that AI systems are designed to be transparent so users understand how decisions are made and explainable so outcomes can be scrutinized and trusted. Additionally, it calls for a commitment to inclusivity, ensuring that AI technologies do not disproportionately disadvantage any particular group. In a nutshell, AI ethics and governance aim to balance technological advancement with societal well-being, creating solutions that enhance human life without causing unintended consequences.
Further reading: Gain trust and transparency with data governance in the age of generative AI.
Why is it important to consider ethics when using generative AI?
Ethics in AI has become a critical concern for organizations, as generative AI and similar technologies have far-reaching impacts on individuals, businesses, and society. International regulations like GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation), CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act), UNESCO recommendations on the ethics of AI, OECD AI Principles, and WHO guidance on AI ethics play a crucial role in shaping the ethical landscape of generative AI. These laws emphasize the protection of personal data, transparency, and accountability, ensuring that AI systems respect privacy rights and prevent misuse.
Ethical considerations of AI help ensure responsible use, foster trust, and minimize unintended harm. Here are the key reasons why ethics matter in generative AI:
- Preventing harm: Generative AI can produce misinformation, biased content, or harmful outputs. Ethical guidelines mitigate these risks and protect users from negative consequences.
- Ensuring fairness: AI systems can unintentionally perpetuate or amplify biases present in training data. Ethical practices promote fairness and inclusivity by addressing these biases.
- Building trust: Transparent and ethical use of AI fosters trust among users, stakeholders, and the public, ensuring the technology is accepted and adopted responsibly.
- Protecting privacy: Generative AI often processes vast amounts of data, raising privacy concerns. Ethical considerations ensure that data is handled securely and that it respects user consent.
- Promoting accountability: Clear ethical standards help define accountability, ensuring developers and organizations take responsibility for AI’s outcomes and impacts.
- Avoiding misuse: Generative AI can be misused for malicious purposes, such as creating deepfakes or spam. Ethical use helps prevent such exploitation.
- Supporting long-term benefits: Ethical AI practices prioritize sustainable development and align with societal values, ensuring that advancements benefit humanity as a whole.
5 foundational pillars for building a responsible generative AI model
Recognizing the need for standards in the ethical use of generative AI is the first step toward responsible implementation. It’s essential to ensure this powerful technology drives positive change for businesses and society while minimizing unintended harm. The ethical considerations when using generative AI demand a proactive approach to identifying and addressing potential challenges before they evolve into real-world issues.
The second step is creating robust policies to guide ethical AI use. This involves understanding the foundational models behind generative AI and building frameworks that align with ethical principles. But what are the pillars of AI ethics that serve as the foundation for responsible practices?
At the heart of ethical AI are five key pillars:
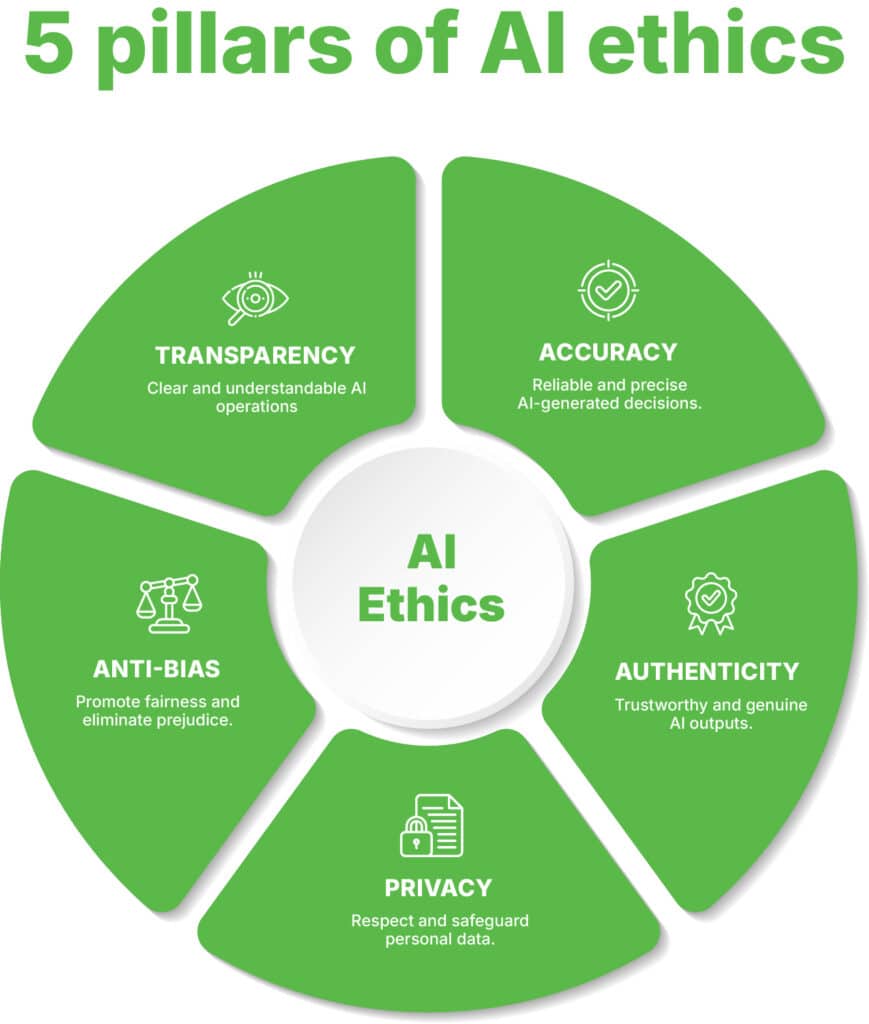
Let’s explore how each of these principles forms the foundation for generative AI ethics, highlighting the responsibility of developers using generative AI.












