Microsoft MPOS technology is a modern point-of-sale system that runs as a Universal Windows Platform (UWP) app on Windows devices. One of the key features of Microsoft MPOS (Modern Point of Sale) is its flexibility and extensibility.
What is an MPOS system?
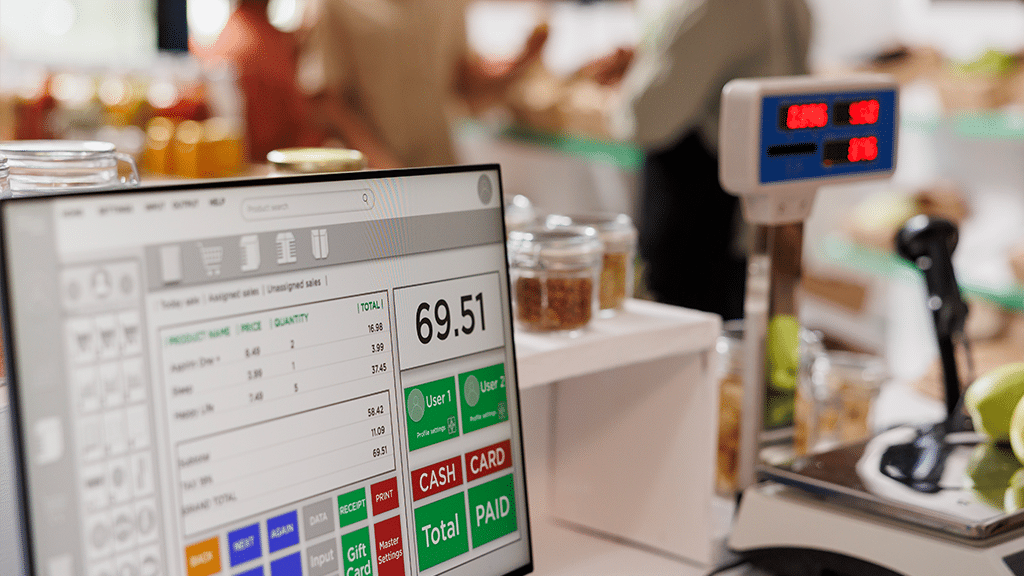
MPOS (Modern Point of Sale) is a component of Microsoft Dynamics 365 for Finance and Operations (F&O) that provides a comprehensive retail management system. MPOS is designed to offer a seamless and efficient point-of-sale experience, integrating various retail operations such as sales, customer orders, inventory management, and more. Here are some key features of MPOS:
- Sales transactions: MPOS allows retailers to handle sales transactions quickly and efficiently, including processing payments, applying discounts, and issuing receipts.
- Customer orders: It supports the creation and management of customer orders, including special orders, layaways, and order fulfillment.
- Inventory management: MPOS provides tools for managing inventory in real time, including stock checks, transfers, and adjustments.
- Customer engagement: It enables personalized customer service by directly accessing customer profiles, purchase history, and loyalty programs from the point of sale.
- Mobility: MPOS is designed to work on various devices, including tablets and smartphones, allowing retail staff to assist customers anywhere in the store.
- Integration: It seamlessly integrates with other Dynamics 365 applications and modules, providing a unified and comprehensive retail management solution. MPOS enhances mobility, efficiency, and customer experience by enabling sales anywhere in the store, reducing wait times, and integrating seamlessly with business operations.
The fundamental workflow of MPOS explained
The Modern POS (MPOS) system operates in two modes: online and offline.
- Online mode: In online mode, the POS client interacts with the Retail Server, which communicates with the Commerce Runtime (CRT) to handle business logic. The CRT processes requests and interacts with the database (DB) to retrieve or store data. The Hardware Station interfaces with peripheral devices like printers and barcode scanners, allowing the POS to control these devices effectively.
- Offline mode: In offline mode, the POS client communicates with the Retail Proxy instead of the retail server. The Retail Proxy handles requests and processes business logic locally, ensuring the POS system continues functioning seamlessly even without a connection to the retail server.
The flow is visually represented in a diagram.
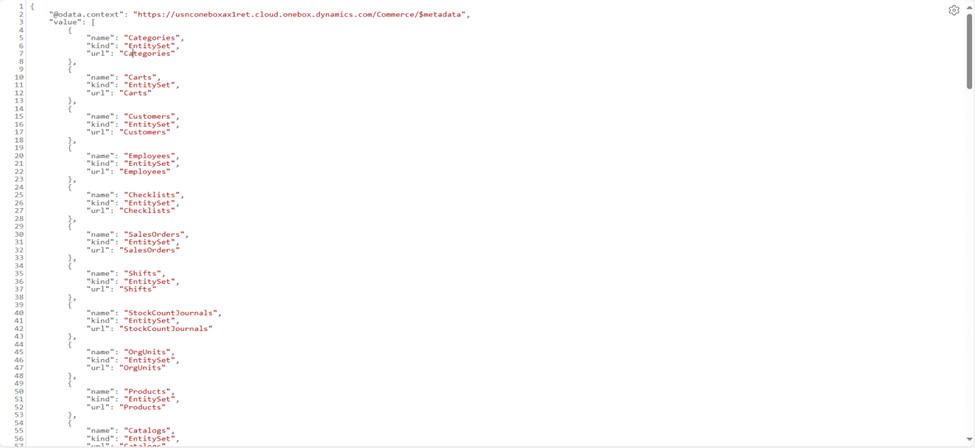
CRT
CRT contains the core business logic written in C# and compiled into .NET assemblies. The POS, as a thin client, relies on CRT for business tasks. It sends requests to the Retail Server, which calls CRT to process and return responses.
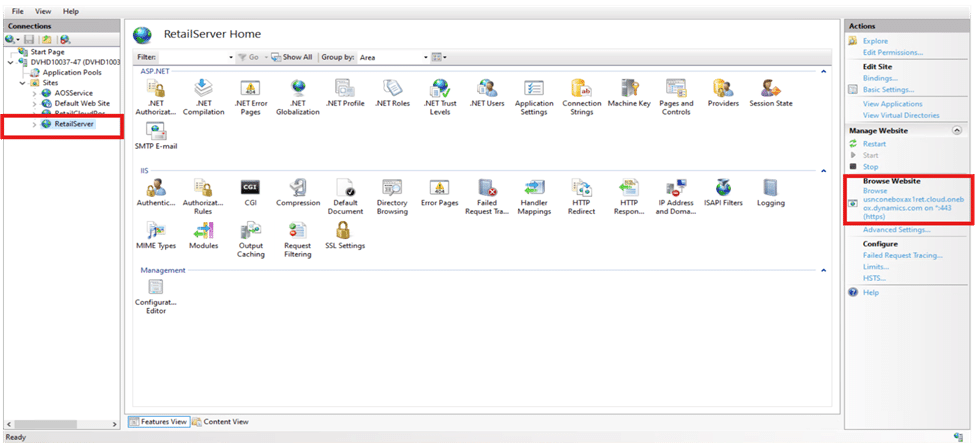
Retail Server
The Retail Server is a middle layer that processes requests from the POS client and calls the Commerce Runtime (CRT) to execute business logic. It then returns the results to the POS, enabling efficient communication and centralized business logic handling.
Retail Proxy
Retail Proxy works similarly to the Retail Server in offline scenarios.
Hardware Station
Hardware Station is the interface where peripheral devices like printers and barcode scanners are attached. The POS client can communicate with and control these devices for seamless hardware integration.
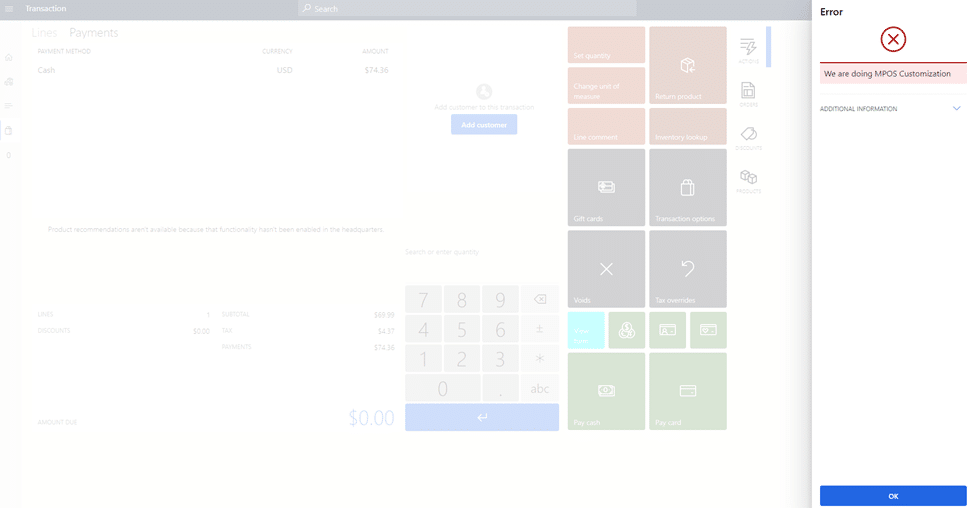
What is MPOS customization?
MPOS customization involves tailoring MPOS systems to fit specific business needs. This includes modifying the user interface, integrating existing software, and adding new features to improve efficiency and user experience. Using the Commerce SDK’s MPOS extension feature, businesses can enhance or change functionalities, add validations, and introduce custom features, making the system adaptable to different retail environments.
In the following areas, we can expand the existing Microsoft MPOS functionality to some extent depending on the business scenario:
- Extend the MPOS user interface (UI): Customizing MPOS involves adding custom columns, app bar buttons, and controls as needed for different views. The screen layout designer can be used to configure the cart view and the welcome page. Customization can be achieved for other views by writing custom code to extend their functionality.
- Override POS business logic: To enhance the business logic of the POS, you can extend it by overriding the POS request handlers. This allows you to incorporate custom logic into the POS system to meet specific business requirements.
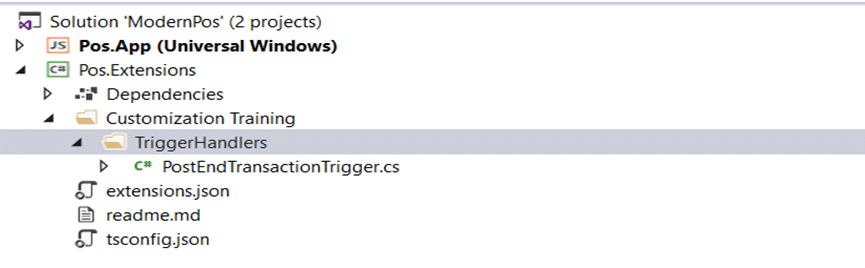
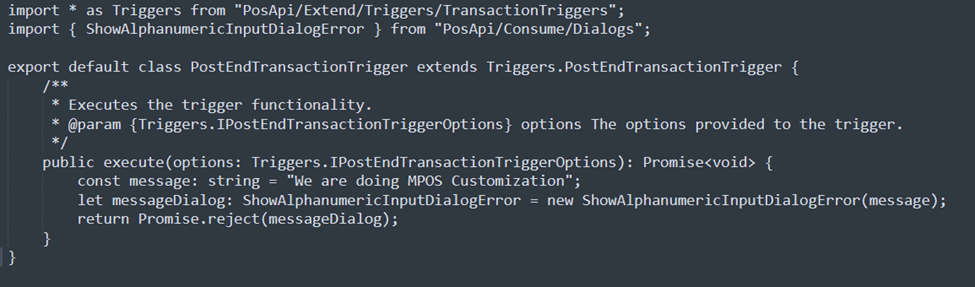
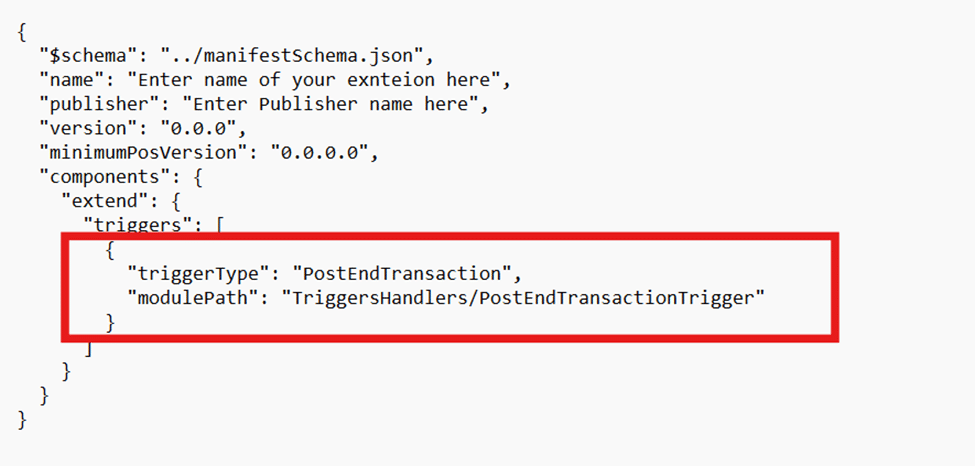
- Add pre-triggers and post-triggers: Enhance the POS system by incorporating custom logic that can be executed before or after any POS operation, allowing for more tailored and flexible functionality.
- Consume APIs: The POS system provides APIs and user experience (UX) controls that can be utilized in extension scenarios. These features enable developers to enhance and customize the POS functionality to specific business needs.
- Add custom operations: Expand the POS system’s functionality by introducing custom operations to perform specific tasks and achieve custom functionality.
For effective MPOS customization, you will need a strong command of C# development language, .NET Framework, JavaScript, Typescript, Knockout.js, HTML, and CSS. Understanding these languages is essential for modifying the user experience, enhancing functionality, and adding custom features.
MPOS customization is essential for businesses aiming to tailor their point-of-sale systems to specific needs. Customization can involve altering the user interface, integrating with existing MPOS software provided by Microsoft, and ensuring the MPOS solutions fit perfectly within your operational framework. Whether adding new features or modifying existing ones, MPOS customization offers the flexibility required to adapt to ever-changing market demands.