In the present digital landscape, data reigns supreme. It is growing in both variety and velocity across different environments, be it on-premises or in the cloud. Recognized as a company’s most valuable asset, the strategic use of data can significantly impact an organization’s success. Ensuring data quality, reliability, and accessibility to the right people at the right time is paramount for informed decision-making. This is precisely where data governance comes into play.
Data governance emerges as the pivotal solution to ensure compliance and security, improve data quality, manage data access, and promote a data-driven culture. Gartner reports that 80% of the organizations that aim to scale their business are likely to fail without a modern approach to data governance. Furthermore, another study suggests that businesses that appoint a designated data governance analyst or data management leader show 42% greater confidence in data quality than those that lack such leadership.
Do you currently have a data governance strategy in place for your organization? This blog sheds light on the significance of data governance, its benefits for businesses, and offers best practices for implementing a robust data governance framework.
What is data governance?
Data governance refers to the overall management of the availability, usability, integrity, and security of data used within an organization. Also, it includes strategies, people, procedures, policies, and standards that ensure effective data management across organizations. Gartner defines data governance as:
“The specification of decision rights and an accountability framework to ensure the appropriate behavior in the valuation, creation, consumption, and control of data and analytics.”
An effective data governance strategy ensures that data is consistent, understandable, trustworthy, and easily accessible for strategic decision-making to improve business outcomes. Without proper governance of data, data integrity and reliability are compromised, posing a significant threat to the organization’s operations and decision-making process. The key goals of data governance include:
- Ensuring, and maintaining the accuracy, consistency, and reliability of data.
- Protecting data from unauthorized access, breaches, or misuse
- Enhancing the value of data
- Appropriate data sharing across the organization
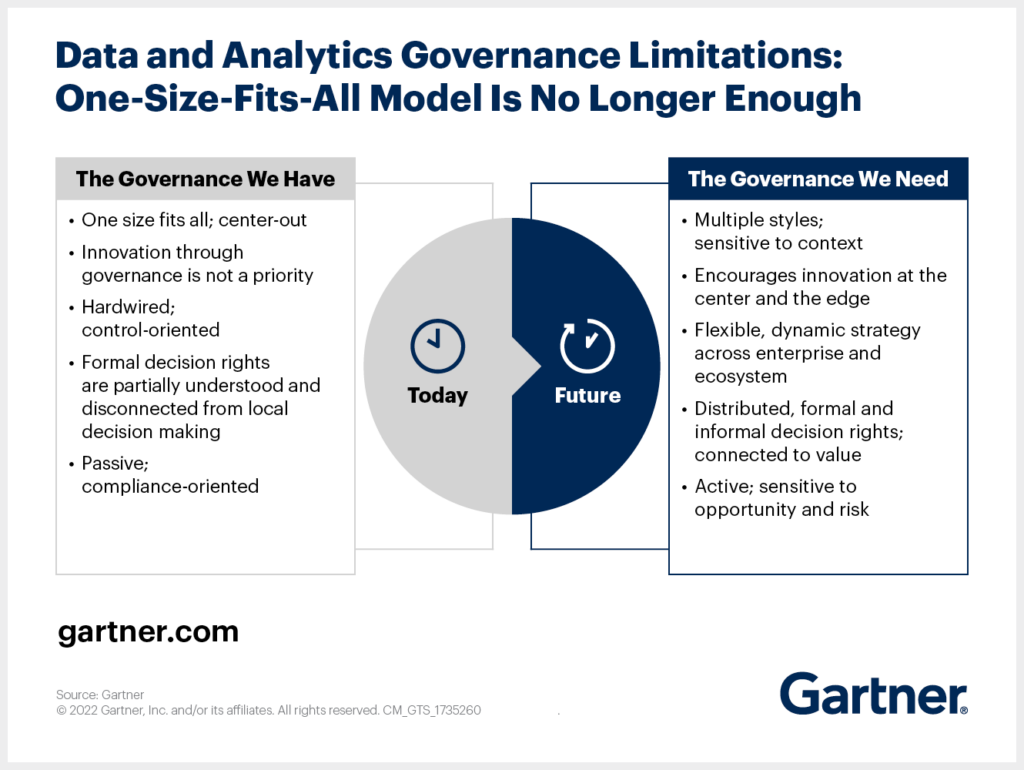
Let’s look at how Gartner explains the current state of data governance and the ideal state that organizations should strive for.
The importance of data governance for business
In the age of data and AI, data governance consulting matters to businesses more than ever. Just as librarians meticulously organize vast collections of books, organizations likewise need structured protocols for effectively managing their business data.
Organizations are more likely to witness data inconsistencies making data management impossible without proper data governance. But the impact goes beyond just that. It also leads to decreased productivity, ineffective decision-making, compliance risk, and legal liabilities for businesses.
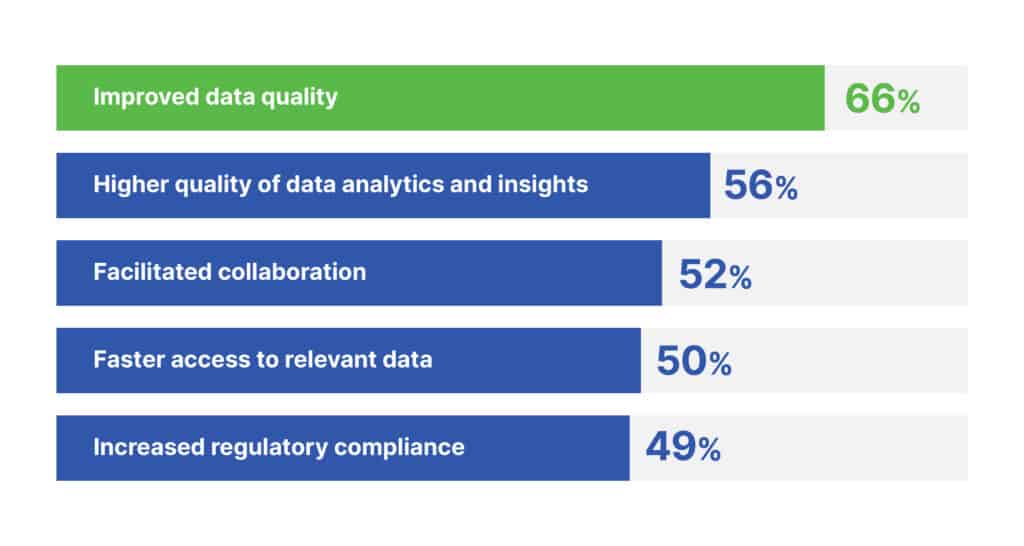
Considering these challenges, implementing a robust data governance framework becomes imperative. Such frameworks not only mitigate risks but also help businesses safeguard their reputation in today’s data-centric environment. Key findings from the Survey of Data and Analytics Professionals show that 83% of organizations with mature data governance program see differences in data quality. Owing to this increased data quality, businesses are more likely to gain a competitive advantage.
The trifecta of data governance framework: People, Process, Technology
Since data governance process involves managing, protecting, and utilizing data, it involves 3 key components: people, processes, and technology. It ensures that data is accurately managed to preserve its integrity, protected from unauthorized access, and used appropriately.
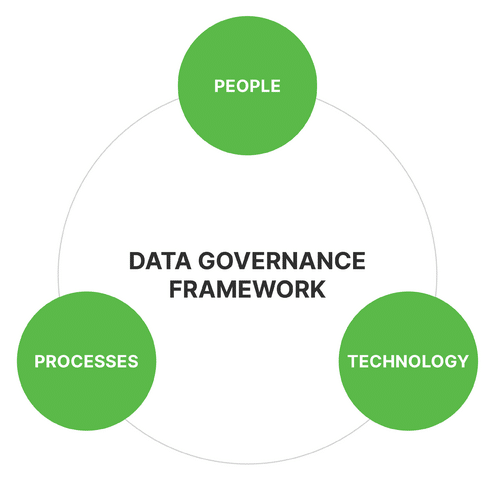
People
This component involves roles, responsibilities, and accountabilities within an organization for creating, collecting, using, and managing data. It includes identifying data owners, data stewards, and data custodians, each of whom has their roles for data security, access, and quality.
Process
This component encompasses the procedures, policies, and methods that govern how data is managed throughout its lifecycle. It includes defining data standards, access controls, quality checks, and lifecycle management practices.
Technology
As the name suggests, this component involves leveraging data governance tools and technologies to support data governance activities. This includes automating data management tasks, tracking data lineage, monitoring data quality, and enforcing data access controls. These tools enhance the efficiency of data governance efforts.
This trifecta of people, processes, and technology lays the foundation for successful data governance and management and helps businesses maximize data to achieve their long-term business goals.