In the rapidly evolving landscape of enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, efficiency drives innovation. Dynamics 365, a platform that empowers businesses to manage operations effectively with its robust architecture and extensive capabilities, is a shining example. However, performance bottlenecks often emerge as data volumes grow, and processes become more complex. This is where multithreading comes into play, offering a powerful tool to optimize execution and improve system efficiency.
In this blog, we will demystify the concept of multithreading in Dynamics 365 X++, exploring its practical applications, implementation strategies, and common challenges. Whether you’re a seasoned developer or just beginning your journey with Microsoft Dynamics 365, this guide will equip you with actionable insights to leverage multithreading effectively in your projects.
What is multithreading in Dynamics 365 Finance and Operations?
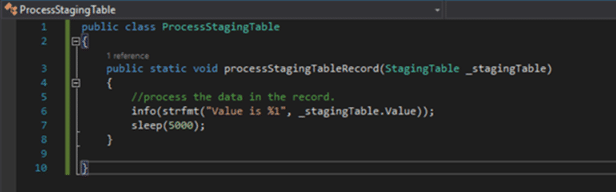
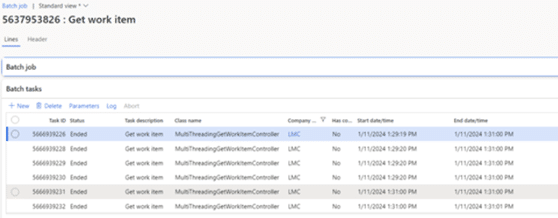
In Microsoft Dynamics 365 Finance and Operations, multithreading refers to the ability to execute multiple tasks or processes simultaneously to improve performance and efficiency, especially during batch processing or data-intensive operations.
Why use multithreading?
Multithreading provides several advantages:
- Improved performance: Tasks are distributed across multiple threads, reducing execution time and enhancing system responsiveness.
- Efficient resource utilization: Tasks are distributed across multiple threads, reducing execution time and enhancing system responsiveness.
- Scalability: By dividing workloads into smaller, independent units, multithreading makes systems more scalable and capable of handling higher transaction volumes.
- User satisfaction: Faster and smoother processes lead to better user experiences, reducing downtime and increasing productivity.
Approaches to multithreading in D365 X++
When implementing multithreading in X++, developers can choose from several approaches, depending on the nature of their tasks. Here are three commonly used methods:
1: Individual task modeling
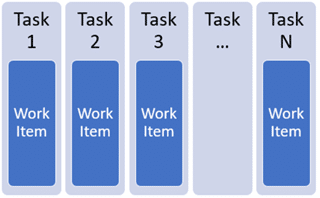
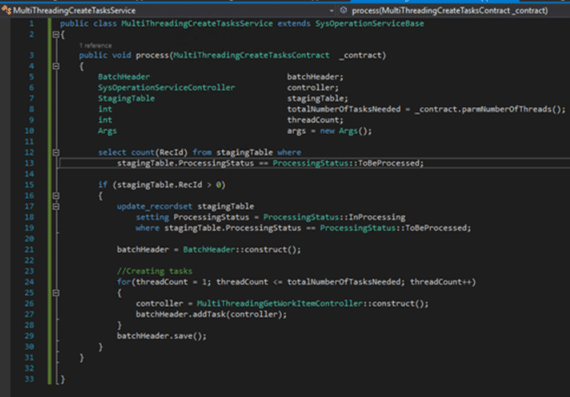
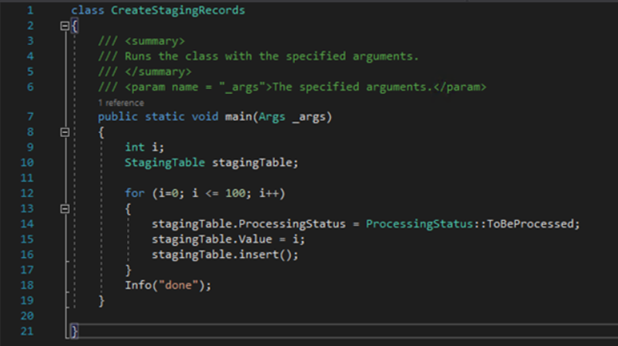
Breaks down large tasks into smaller, independent work items that can be processed in parallel.
Use the BatchHeader and BatchJob classes to define and execute these tasks.
2: Batch bundling
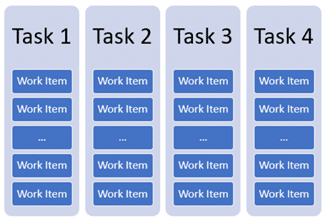
Groups similar tasks into bundles and process them as a single batch. This method is ideal for scenarios where tasks share common data or dependencies.
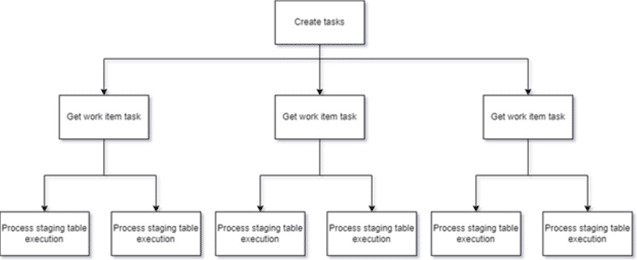
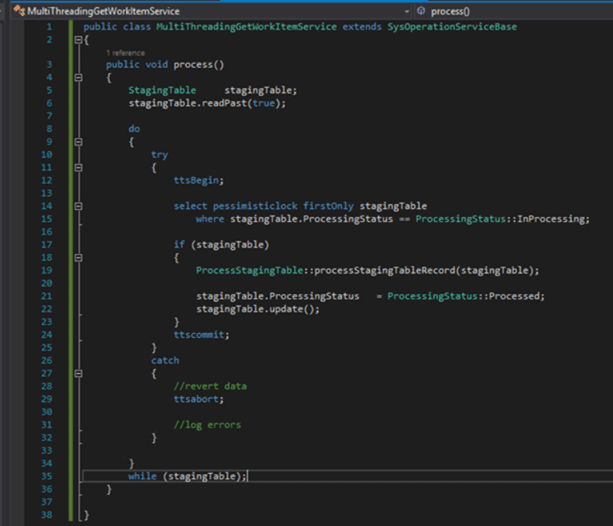
3: Top-picking pattern
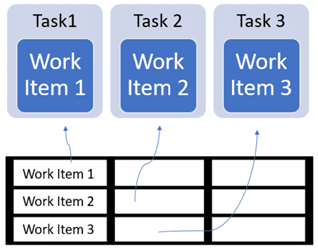
Assign tasks dynamically based on workload distribution. It’s useful for scenarios where task priorities or data availability vary over time.
Each approach offers unique advantages, and the choice depends on factors like task complexity, data volume, and system constraints.
The role of Batch Framework and SysOperation Framework
Dynamics 365 provides robust frameworks to facilitate multithreading: the Batch and SysOperation frameworks. These tools enable developers to distribute tasks across multiple threads and process them in parallel.
Batch framework
The Batch Framework is designed to schedule and execute tasks in the background. Each task within a batch job can be processed on a separate thread, making it an ideal choice for multithreaded operations. Key features include:
- Automatic load balancing across threads.
- Fault tolerance for retrying failed tasks.
- Ability to schedule jobs at specific times.
SysOperation framework
The SysOperation Framework, a newer model, builds on the Batch Framework and introduces additional benefits:
- Separation of business logic and execution logic.
- Enhanced scalability for large workloads.
- Support for parameterized task execution.
Both frameworks provide a solid foundation for multithreading in Dynamics 365, enabling developers to handle even the most demanding scenarios effectively.